Student library at the University of Basel © University of Basel
Education System
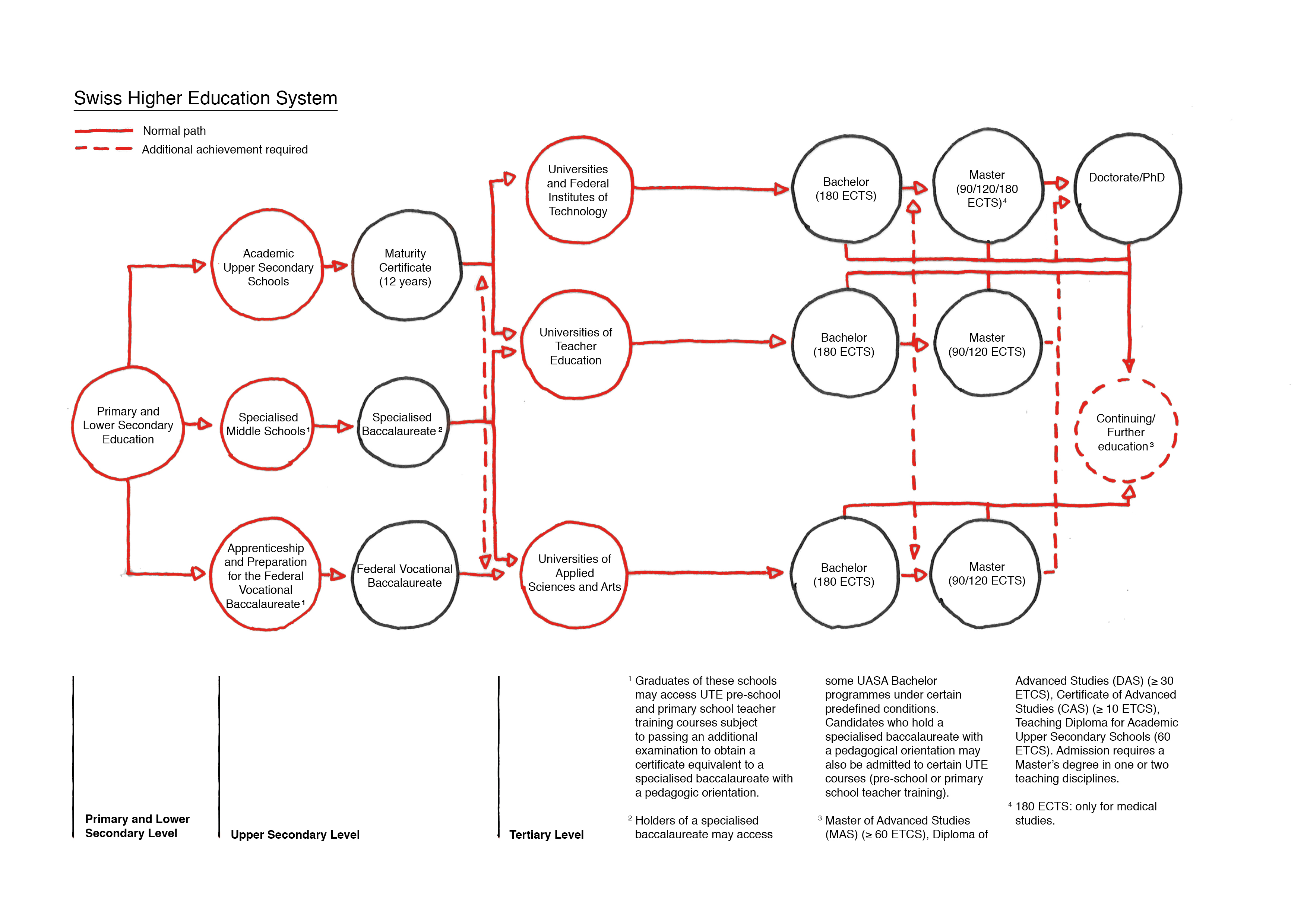
The Swiss education system can be divided in three main parts: compulsory education, upper secondary level and tertiary level. A specificity in Switzerland is the high degree of permeability: there are different ways to reach your goal and you can switch easily from one to the other! Let’s look at it from top to bottom.
Tertiary Level
Higher education forms the tertiary level. In order to qualify for this level, you have to get an upper secondary degree (maturity certificate). You’ve got one? Great! So, you have to choose between:
- professional education and training colleges – which enable professionals who have completed vocational education and training to specialize and to enhance their skills and knowledge; and
- the universities – which offer various academic and practice-oriented programmes
You’re interested in studying at university level?
Then you’re in the right place on this website! But which sort of tuition are you looking for? Depending on what you want to become, you will choose to go to a:
These are the three different types of universities in Switzerland.
Upper Secondary Level
At this level, the responsibility is divided through the cantons and the Confederation.
After the compulsory education, students have the opportunity to choose an apprenticeship. The majority of the week (three or four days) is spent working in a company (practical learning) and the rest of the week is spent in a vocational school (one or two days): this is the dual-track system. At the end of their professional training, students receive a VET (vocational education and training) certificate. They can also conclude the apprenticeship with a federal vocational baccalaureate.
Students can also study in a middle school/high school or in an upper secondary specialised school. At the baccalaureate school (Gymnasium/gymnase), they will receive a “maturity certificate”. In upper secondary specialised school, they will receive a “specialised baccalaureate” (Fachmaturität/maturité spécialisée). These schools prepare the students for further education at the tertiary level.
Compulsory Education: Primary and Lower Secondary Level
Public compulsory education is free. It usually takes 11 years to complete compulsory schools: eight years at primary school (including two years of first learning cycle) and three years of secondary school. Some differences may exist between the different cantons. The 26 cantons are responsible for compulsory education. Each local municipality organizes the schools and daily work. The language of instruction is French, German, Italian or Romansh, depending in which part of Switzerland the school is located. Pupils enjoy mandatory classes in a 2nd national language and in English.